Root Cause Changes (RCC)
Root Cause Changes (RCC) dramatically speeds up the process of identifying the changes that cause outages and incidents in your systems.
By integrating your CI/CD and change management tools with BigPanda, you can normalize and aggregate change data alongside incidents. This comprehensive enrichment gives you deep insights into the changes that may have triggered an issue.
BigPanda analyzes each change against active existing incidents in real-time, so your teams don’t have to manually dig through hundreds or thousands of potentially related change events. Changes that are suspected as a potential root cause are flagged and added to the incident.
The Changes Tab
RCC uses an algorithm based on natural language processing and vector space models to compare changes to active incidents. This allows BigPanda to identify the connections between alerts and change data with confidence that suspected changes are statistically relevant.
BigPanda University Advanced Insight Module course
Learn more in the BigPanda University Advanced Insight Module course.
By the end of the course you will be able to:
Generate and review AI Analysis reports for your incidents that will help you reduce MTTR.
Review root cause change suspects and identify changes that are the root cause of incidents.
Compare incidents with similar characteristics to enhance context and resolve incidents faster.
Click here to enroll.
Key Features
Connect a variety of change tools to BigPanda using standard and custom integrations.
View changes that occurred prior to and during an incident to easily identify changes that may have been related to the incident.
Visualize metrics related to change data using dashboards in Unified Analytics.
Analyze suspected root causes more easily with AI-generated summaries.
Changes (RCC) API
Root Cause Changes can also be viewed and managed with the Changes (RCC) API.
Integrate Changes with BigPanda
Change integrations give your Operations teams deeper insights into the system changes that may be triggering system events and outages. This gives Operations teams clear visibility into changes pushed by Developers, empowering the two teams to collaborate more proactively and effectively.
BigPanda includes several standard change integrations ready to connect your change feeds to BigPanda. You can also build custom integrations with the Root Cause Changes (RCC) REST API.
Learn more about integrating your change tools with BigPanda in the Integrate with BigPanda documentation.
Changes in the BigPanda Incident Console
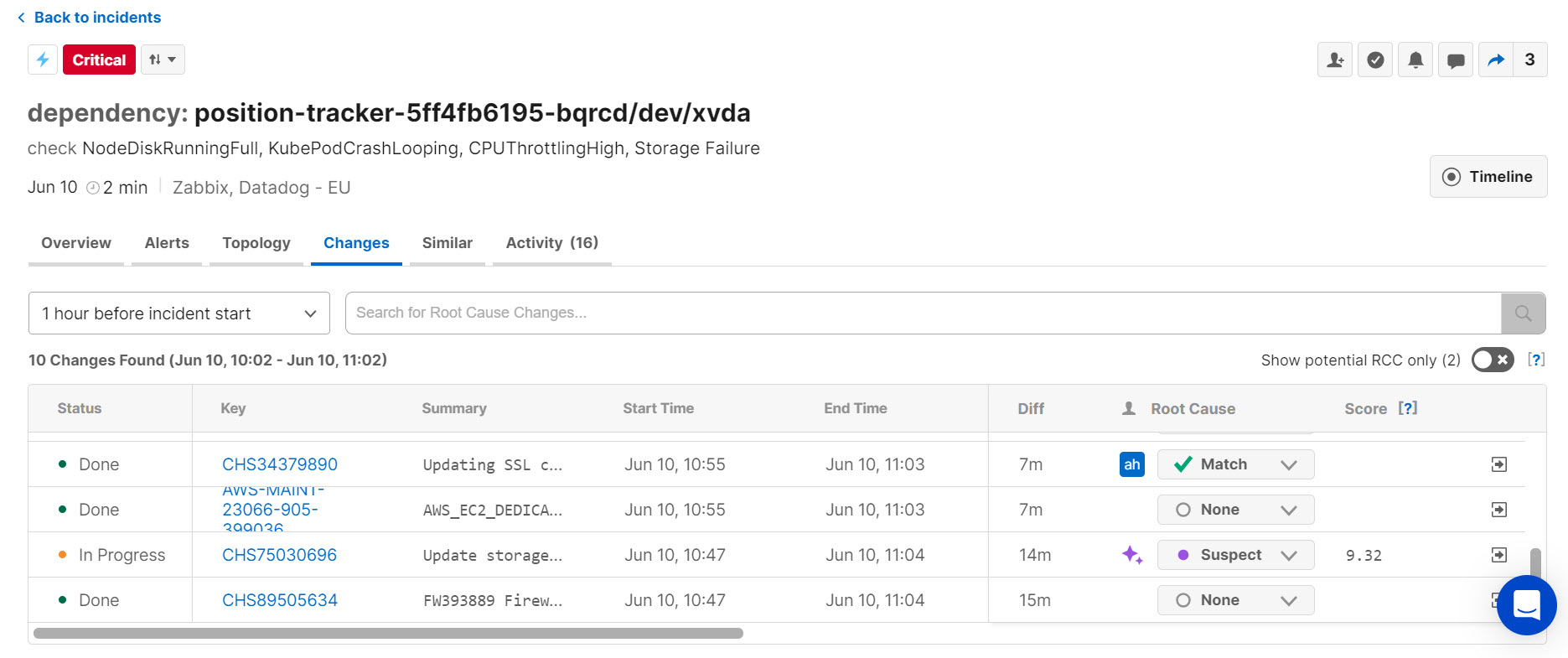
Changes that occurred shortly before or during the incident are displayed in the incident details pane within the Changes Tab. Here operators can see vital information about changes that are possibly related to the selected incident, including status, summary, and start time.
Change Details
Operators can search the change table, dig into change details, and mark whether a change should be matched to the incident. By marking the results of change investigation in the console, teams can collaborate together to identify the real cause.
BigPanda will automatically compare change data to incoming incidents, looking for potential incident causes. If a change is highly correlated with an incident, it will appear as a Suspect in the incident details pane. A description will explain what details indicate the change may be related to the ongoing incident. While BigPanda is configured to suggest up to 5 related changes, only changes that are highly correlated will be suggested.
RCC in ServiceNow
Root Cause Changes can also be configured to appear within ServiceNow. See the AI Detection and Response for ServiceNow documentation for more information.
Show potential RCC only
Use the Show potential RCC only toggle to limit the change table to only show changes BigPanda has identified as RCC suspects.
Viewing suspects in the Incident Feed
Incidents containing a suspected root cause change are marked in the Incident Feed with a purple dot.
Hover over the purple dot to see how many suspected changes are flagged in the incident. To view more details, click on the incident and navigate to the Changes tab in the incident pane.
Merging incidents with suspected root cause changes
If you merge an incident and the source incident contains a change marked as a suspected root cause, the purple Suspect marker will be added to any matching changes in the destination incident.
Learn more about how operators can leverage changes in the BigPanda console in the Remediate Incidents documentation.
Suspected Root Cause Summary
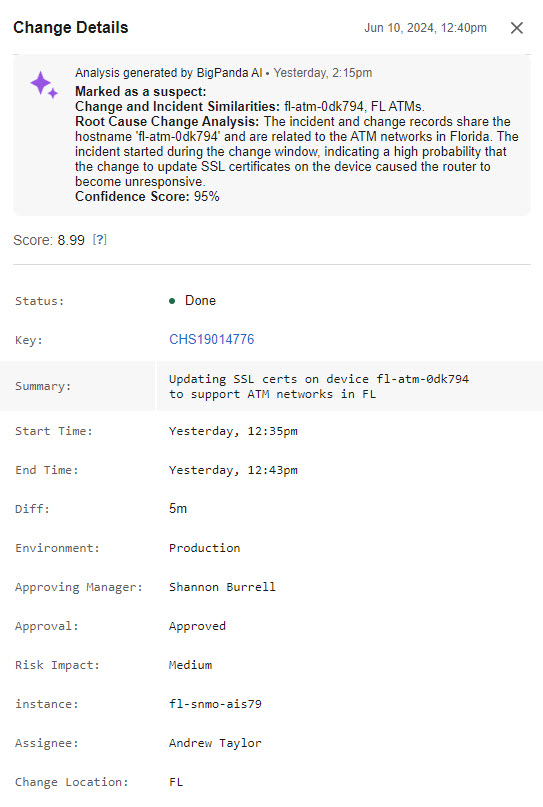
Any environments configured with Automated Incident Analysis will automatically include an AI-generated explanation for why BigPanda marked a change as a potential root cause. This easy-to-read explanation provides more context and better insights into matches, saving you time as you hunt down the root cause of an incident.
To view this summary:
Click on an incident to access the incident details pane.
Scroll down to Potential Root Cause Changes.
Click on the change you want to investigate.
The automated explanation will be at the top of the Change Details panel.
You can also view this information by navigating to the Changes Tab within the incident details pane. From there, click on any change with the purple stars beside it, as this indicates a change that BigPanda has automatically suggested as a potential root cause change.
Automatic Root Cause Changes Suspects
Root Cause Changes (RCC) leverages an algorithm based on natural language processing and vector space models. BigPanda intuitively compares the complex and discordant data from monitoring and change tools, while considering the context and timing of causal relationships.
RCC runs calculations on key connections between incidents and changes, including:
Time Frame - how close were the change and incident
Alerts Coverage - how many of the alerts match properties in the change
Categories - groups of specific details defined for weighting and parsing matches
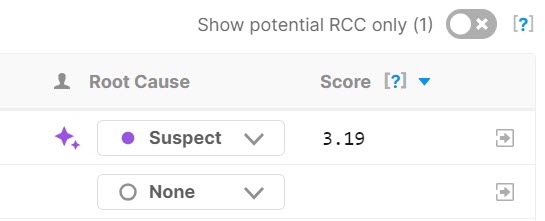
Each incident-change match is given a causation score based on these calculations, with a higher score indicating a more likely suspect. Changes with a high causation score are surfaced in the incident details pane as RCC Suspects.
Suspect Score
Score calculation
Change suspect causation scores do not have an upper limit. Each suspect match point gets added to the score. Higher scores indicate a stronger match and can assist in determining the most likely suspect.
Scores only appear for matches that have met the threshold in your RCC configuration. To adjust your RCC configuration, contact BigPanda Support.
To set a baseline of your scores and monitor trends, see the Suspected Changes Analysis dashboard in Unified Analytics.
Time Frame
RCC is focused on finding causation, not correlation. Only changes that have been implemented long enough to create a system event and scheduled change windows that have recently started are considered as potential causes.
Changes that happened too far before the incident are also excluded, as incidents usually happen shortly after system changes.
Alerts Coverage
Many incidents will have at least one alert that matches the data for recent changes. When only a single alert matches, the relationship between the incident and change may not be causal, especially in complex incidents with multiple downstream impacts.
To help identify strong causal relationships, RCC considers the percentage of alerts in an incident that align with the change details. Higher percentages indicate a closer connection between the incident and change.
Categories
RCC uses change details, alert tags, and incident metadata to find common values between incidents and changes.
However, not all matches imply strong connection or potential cause.
To consider the context and relationships between data, RCC breaks incident data into a hierarchy of categories weighted by importance, based on expected incident and change alignment. Different weights and parsing rules apply to tag matches in each category, making sure that matches reflect the relationship of shared system attributes and resources.
Your default RCC category configuration is built on common industry practices, system topology, and tags and processes unique to your organization.
Improving Root Cause Changes Results
RCC works best when it has rich data and meaningful relationships identified for your organization.
It's easier for BigPanda to spot causality accurately when more standardized information is available in incoming tags and description fields. If you’d like to improve your RCC results, high quality enrichment and tag normalization is an important start.
For even more refinement of results, you can request modifications to your RCC category and parsing configuration. This is a complex back-end process requiring close coordination with BigPanda support. Reach out to us at [email protected] if you are interested in adjusting your RCC configuration.
Reporting on Root Cause Changes
The Unified Analytics Root Cause Changes (RCC) dashboards help users measure and improve change management and investigation. Interactive dashboards show change details alongside alerts and incidents, allowing users to visualize these metrics over time, services, and infrastructure.
The Change Analysis Dashboard is designed to help you visualize trends and patterns in change data. It also helps you measure the maturity of change processes and the quality of change data. Use this dashboard to identify which source systems are sending changes in order to optimize your BigPanda change integrations, spot recurring issues and improve your change processes to ensure optimal outcomes with RCC.
The Suggested Changes Analysis Dashboard focuses on RCC matches and incident coverage. Use this dashboard to determine the effectiveness of your root cause changes configuration and to determine next steps for reducing MTTR.
Next Steps
Learn more about BigPanda's Incident Intelligence
Dig deeper into Correlating Changes with Incidents
Begin integrating Change Integrations